Syndis has observed a significant increase in cyberattacks in recent months. Incidents are now occurring on a monthly or even weekly basis where attackers have successfully breached the IT systems of Icelandic companies. These attacks come in various forms, including email inbox intrusions, breaches of web systems, interception of communications, credential phishing, and most notably—ransomware attacks.
What Is Ransomware?
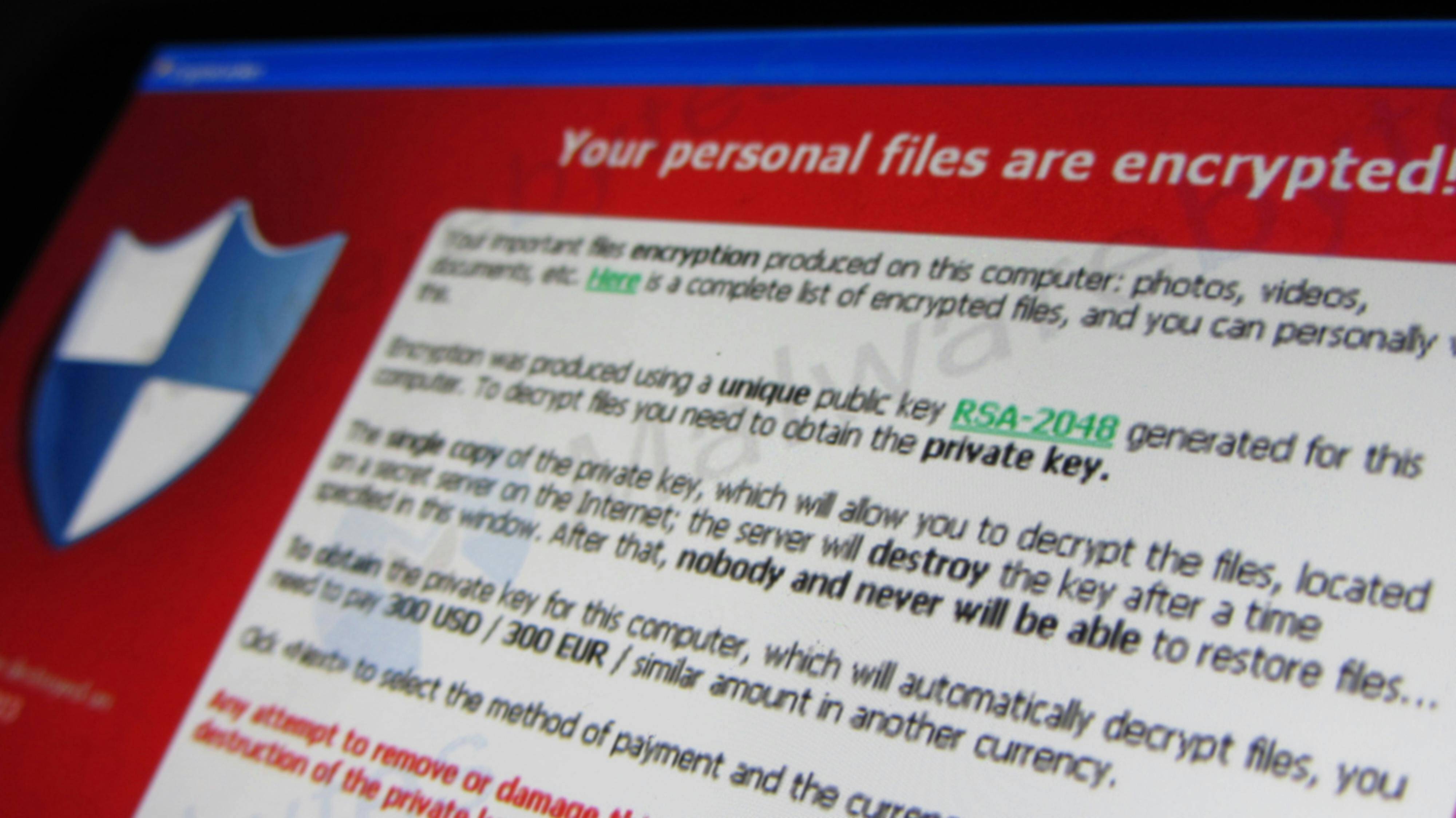
Ransomware is a type of cyberattack where a victim’s data is encrypted, making it inaccessible to system owners. The attacker then demands a ransom—often in the tens or hundreds of millions of ISK—to provide a decryption tool that restores access.
The impact is typically severe: within minutes or hours, most or all IT systems are disabled. Recovering to full operational status can take extensive effort. While core systems may be restored within hours or days, full recovery depends heavily on the condition and availability of backup systems post-attack.
Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures (TTPs)
Ransomware investigations focus on identifying the Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures (TTPs) used by attackers (see MITRE ATT&CK). These vary by group. In some cases, one group gains initial access and sells it to another group specializing in data theft or ransomware deployment.
Attack Execution
Victims are typically selected based on internet-exposed systems and known vulnerabilities. For example, an attacker might specialize in exploiting a particular type of firewall and scan the internet for systems matching that profile. Once a vulnerability is found, the attacker attempts to breach the perimeter firewall—the organization’s first line of defense.
After initial access, the attacker seeks to escalate privileges, often targeting server administrator rights, while simultaneously exploring the network to identify further attack vectors. They may deploy tools to exploit weaknesses such as:
-
Credential server vulnerabilities (e.g., ESC1, ESC8)
-
Active Print Spooler on domain controllers
-
Disabled SMB signing
-
Outdated operating systems (e.g., Windows Server 2000–2012, Windows XP, Win7)
-
Administrators using weak passwords
Establishing Persistence
Once inside, attackers often install backdoors—ways to return unnoticed even if the initial breach is detected. Simultaneously, they map out the environment to decide whether to deploy ransomware, exfiltrate data, or both.
Data theft may occur via:
-
FTP servers
-
Cloud storage
-
RDP-based file transfers
-
Compressed archive files to streamline exfiltration
The Ransomware Trigger
When the attack is ready, the ransomware is activated. Data is encrypted rapidly—not the full file, but just enough of the beginning and end to render documents, databases, and applications unusable. A text file is left behind, explaining what has happened, how to contact the attackers, the ransom amount, and payment instructions.
Communicating with the attackers is not advised without careful consideration. Such contact can signal desperation, and may result in:
-
The organization being publicly listed as a victim on dark web leak sites
-
Stolen data being released or sold
Organized Crime
These attacks are often part of organized criminal operations. For instance, according to CISA, one group reportedly received $42 million USD (nearly 5.5 billion ISK) in ransom payments from over 250 companies within just nine months (March–December 2023).
Given the massive financial incentives, it is unlikely that ransomware operations will stop anytime soon. Strengthening cyber defenses is therefore critical.
Strengthening Resilience
Organizations must implement layered defenses to slow attackers down, even if initial barriers are breached. Examples include:
-
Timely patching of all systems
-
Segmentation of internal networks
-
Strong endpoint protection
-
Restricting administrative access
-
Educating employees on phishing and social engineering